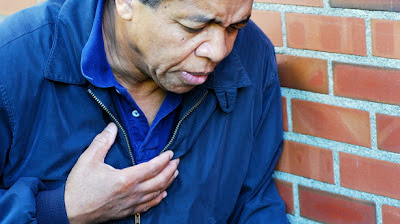
Many people use heart attack and cardiac arrest interchangeably, but they are actually two entirely different medical conditions. Here are the differences between the two.
Heart attacks are usually painful attacks that are caused by blockage of the arteries that send blood to the heart. The medical term for heart attack is myocardial infarction. Many people do not recognize the symptoms of heart attacks and may wait hours before going to the emergency room.
Seeking medical attention as soon as possible is critical as this may prevent further damage to the heart and possible death. During a heart attack, the patient is awake and the heart continues to beat
Cardiac “arrest” means just that. The heart is arrested, or stops beating. This is known as sudden cardiac arrest. Patients are also in cardiac arrest when they collapse and their breathing is abnormal. Without CPR and immediate medical treatment, patients in cardiac arrest can die within just minutes. When a person collapses, is unresponsive, and is not breathing normally, they are most likely experiencing sudden cardiac arrest. Whether or not the victim survives depends largely upon the immediate response by those in close proximity to the victim to keep the heart beating.